News information
Location:Home - News - Industry news
30 technical data that Hydronics should know
2022-10-12
1. Several practical data that should be understood:
(1) Indoor heating meets the standard temperature of 18 ° C;
(2) The heating load of the building area is 40-60kcal/h · m2 (45-70W/m2);
(3) The reasonable flow rate required for heating the building area is 2.5-3.5 kg/h · m2 (1-2 kg/h · m2 for energy-saving buildings);
(4) The total supply and return water temperature of the external network during the severe cold period of the primary network is 55-70 ° C;
(5) The water replenishment amount of the heating network should be less than 0.5% of the circulation amount of the heating network;
(6) One ton of heat can supply a building area of 1-15000 square meters (energy-saving buildings of 20-30000 square meters);
(7) The motor power of the circulating pump per 10000 square meters of building area is generally between 3-5 kW;
(8) Some advanced heating enterprises only consume 0.7-1.2 yuan per square meter of electricity per square meter during the heating period with circulating water pumps in their heating networks. However, many enterprises have surpassed advanced enterprises by 3-4 times, resulting in severe waste of electricity.
1. Several practical data that should be understood:
(1) Indoor heating meets the standard temperature of 18 ° C;
(2) The heating load of the building area is 40-60kcal/h · m2 (45-70W/m2);
(3) The reasonable flow rate required for heating the building area is 2.5-3.5 kg/h · m2 (1-2 kg/h · m2 for energy-saving buildings);
(4) The total supply and return water temperature of the external network during the severe cold period of the primary network is 55-70 ° C;
(5) The water replenishment amount of the heating network should be less than 0.5% of the circulation amount of the heating network;
(6) One ton of heat can supply a building area of 1-15000 square meters (energy-saving buildings of 20-30000 square meters);
(7) The motor power of the circulating pump per 10000 square meters of building area is generally between 3-5 kW;
(8) Some advanced heating enterprises only consume 0.7-1.2 yuan per square meter of electricity per square meter during the heating period with circulating water pumps in their heating networks. However, many enterprises have surpassed advanced enterprises by 3-4 times, resulting in severe waste of electricity.
2. The internal resistance of hot water boilers is generally 8-10mH2O.
3. The range of boiler flow variation is ± 10%, which is 90-110% of the rated flow.
4. The normal resistance range of the plate heat exchanger system should be between 5-7mH2O.
5. The temperature difference between the supply and return water of the heating primary network should be 40-50 ° C, and currently the industry generally maintains it at 20-35 ° C; The temperature difference of the secondary network should be 20-25 ° C, and the current operating level of the domestic industry is between 15-20 ° C.
6. The economic specific friction of the main line and branch line should be between 30-70Pa/m. The pipe diameter of the branch line and branch line should be determined based on their service pressure, but the hot water flow rate should not exceed 3.5m/s, and the specific friction should not exceed 300Pa/m.
7. The flow velocity of indoor pipelines in civil buildings should not exceed 1.2m/s.
8. The most unfavorable specific frictional resistance of the indoor system should be set at 60-120Pa/m, and the relative difference in calculated pressure loss between the most unfavorable loop and each parallel loop should not exceed ± 15%; The total calculated pressure loss of the entire hot water heating system (indoor) should be increased by 10% of the added value.
9. Continuous operation has better operating efficiency than intermittent operation of boilers. In the winter of 1983, the heating research laboratory of Harbin Institute of Architecture and Engineering conducted an intermittent operation test on a reciprocating grate hot water boiler. The boiler efficiency was 57% in the first hour of heating up, 64.5% in the second hour, and stabilized at 76% in the third hour.
10. A high boiler load rate results in high boiler efficiency.
11. The service life of the heating network should be 30 years, and it is 30-50 years abroad.
12. The setting of domestic hot water above 55 ° C is based on the presence of bacteria; Less than 60 ° C is considered for scaling.
13. For media below 150 ° C and well insulated pipeline networks, the temperature drop should not exceed 0.5 ° C/Km.
14. Pump efficiency η= Between 75 and 85%
1m · m3/h=2.78W (i.e., the net power to increase 1 ton of water by 1 meter per hour is 2.78W)
Shaft power=net power ÷ η
Motor power=1.05-1.2 shaft power
15. Quality of polyurethane insulation:
Compressive strength above 0.2MPa
Density 50-60Kg/m3
Water absorption ≤ 0.2 Kg/m2
Closed cell rate>40%
Thickness deviation ± 5%
Eccentricity less than 5%
16. The heating load is directly proportional to the indoor and outdoor temperatures:

Special case: when tn=18 ° C
Tw1=-11 ° C
When tw2=-10 ° C
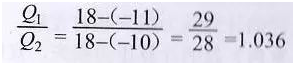
That is, for every 1 ° C decrease in outdoor temperature, the heat needs to increase by 3.6%.
Similarly, for every 1 ° C increase in indoor temperature, heat needs to increase by 3.6%. (Data varies in different regions)
17. The relationship between radiator heat dissipation and hot water temperature:
Q=2.04 Δ T1.28( Δ t: The difference between the average temperature of the radiator and room temperature
When Δ Q1=422W/piece at t1=64.5 ° C
When Δ Q2=340W/piece at t2=54.5 ° C
That is, for every 10 ° C decrease in the temperature of the heating medium, the heat dissipation decreases by 20%
That is to say, when the temperature of the heating medium drops by 1 ° C, the heat dissipation decreases by 2%
Four pillars 813, Q=0.627 Δ T1.302
When Δ When t1=64.5, Q1=114.3W/piece
When Δ When t2=54.5 ° C, Q2=340W/piece
18. An indoor increase of 1 ° C (or an outdoor decrease of 1 ° C) results in an average water temperature increase of about 2 ° C.
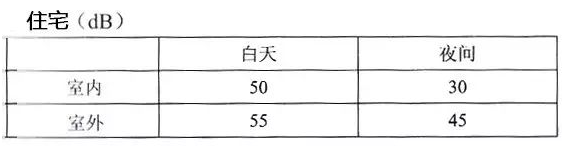
19. The World Health Organization (WHO) published a noise limit guideline in 1993.
20. Cooling load index: 30-50W/m
20. Cooling load index: 30-50W/m2, with a maximum of 70W/m2.
21. Household heat metering: The resistance of the building's heat inlet system (due to the installation of a heat meter indoors, the resistance is about 30KPa) is about 50KPa.
22. Compared with conventional radiators, floor heating has a greater heat storage capacity, which is manifested by the hysteresis of heat exchange. From system startup to the required room temperature, the radiator takes 1-2 hours, while floor heating takes 3-5 hours.
23. Compared with conventional radiator heating, floor heating has a room temperature 2-3 degrees lower under the same comfortable conditions as the human body.
24. Although the pipes inside the heat source are very short, it should be noted that there are many local resistance components such as elbows and valves. The inlet and outlet connecting pipes of the pump should be one to two sizes larger than the inlet diameter of the pump. The diameter of the connecting pipe inside the heat source should be as large as possible, and it is recommended to have a specific frictional resistance between 30 and 70Pa/m, so that the internal resistance of the heat source is less than 0.15MPa.
25. The water supply temperature for floor heating is generally between 35-50 ° C (with a maximum temperature not exceeding 60 ° C), and the difference in water temperature between supply and return generally does not exceed 10 ° C; - The design supply and return water for general radiator heating is 80/55 ° C, and the actual operating water supply is generally between 55 and 70 ° C, with a water temperature difference of about 15 ° C.
When calculating the heat load of a comprehensive floor radiation heating system, the indoor calculated temperature should be taken as 2 ° C lower than the indoor calculated temperature of a convection heating system, or 90% to 95% of the total heat load calculated by the convection heating system.
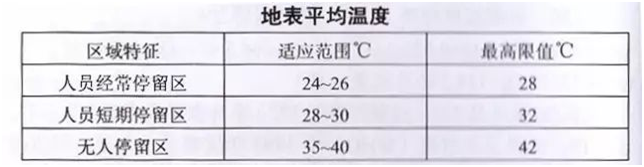
27. The calculated average surface temperature should comply with the provisions of the table below.
20. Cooling load index: 30-50W/m
20. Cooling load index: 30-50W/m2, with a maximum of 70W/m2.
21. Household heat metering: The resistance of the building's heat inlet system (due to the installation of a heat meter indoors, the resistance is about 30KPa) is about 50KPa.
22. Compared with conventional radiators, floor heating has a greater heat storage capacity, which is manifested by the hysteresis of heat exchange. From system startup to the required room temperature, the radiator takes 1-2 hours, while floor heating takes 3-5 hours.
23. Compared with conventional radiator heating, floor heating has a room temperature 2-3 degrees lower under the same comfortable conditions as the human body.
24. Although the pipes inside the heat source are very short, it should be noted that there are many local resistance components such as elbows and valves. The inlet and outlet connecting pipes of the pump should be one to two sizes larger than the inlet diameter of the pump. The diameter of the connecting pipe inside the heat source should be as large as possible, and it is recommended to have a specific frictional resistance between 30 and 70Pa/m, so that the internal resistance of the heat source is less than 0.15MPa.
25. The water supply temperature for floor heating is generally between 35-50 ° C (with a maximum temperature not exceeding 60 ° C), and the difference in water temperature between supply and return generally does not exceed 10 ° C; - The design supply and return water for general radiator heating is 80/55 ° C, and the actual operating water supply is generally between 55 and 70 ° C, with a water temperature difference of about 15 ° C.
When calculating the heat load of a comprehensive floor radiation heating system, the indoor calculated temperature should be taken as 2 ° C lower than the indoor calculated temperature of a convection heating system, or 90% to 95% of the total heat load calculated by the convection heating system.
27. The calculated average surface temperature should comply with the provisions of the table below.
28. The working pressure of the low-temperature hot water floor radiation heating system should not exceed 0.8MPa; When the height of a building exceeds 50m, it is advisable to set up vertical partitions.
29. Main parameters of the thermostatic valve: nominal pressure 1MPa; Maximum pressure difference 0.1 MPa; Adjust the scale from 0 to 5; Temperature adjustment range 8~28 ° C; (Product execution standard JG/T195-2007)
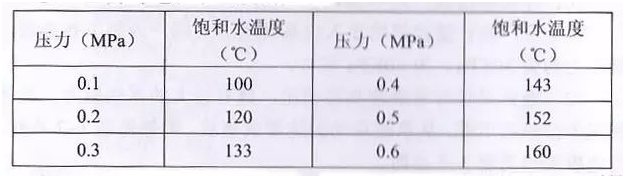
30. Relationship between pressure and saturated water temperature: